A sound grasp of data and its interpretation is pivotal to decision-making in every business operation. With the bombardment of data in this digital age, the essence of visual representation and interpretation of data cannot be overstressed. In this article, we will discuss one such powerful data representation tool: the combination chart.
The Core Concept of a Combination Chart
What is a combination chart? Simply put, a combination chart is an amalgamation of two or more charts into a single chart, thereby allowing multiple data sets to be compared on a single axis. This feature enhances your data visualization by providing a nuanced understanding of complex data scenarios.
Combination charts are designed to enhance your data visuals while promoting clear, concise correlation among diverse data sets and variables. They are a powerful tool in data analysis, and efficiently so because they condense multiple metrics into manageable visualizations.
Most importantly, combination charts streamline the decision-making process as they provide a holistic view of correlating the components and their interdependence in an entire business operation.
Different Types of Combination Charts and Their Composition
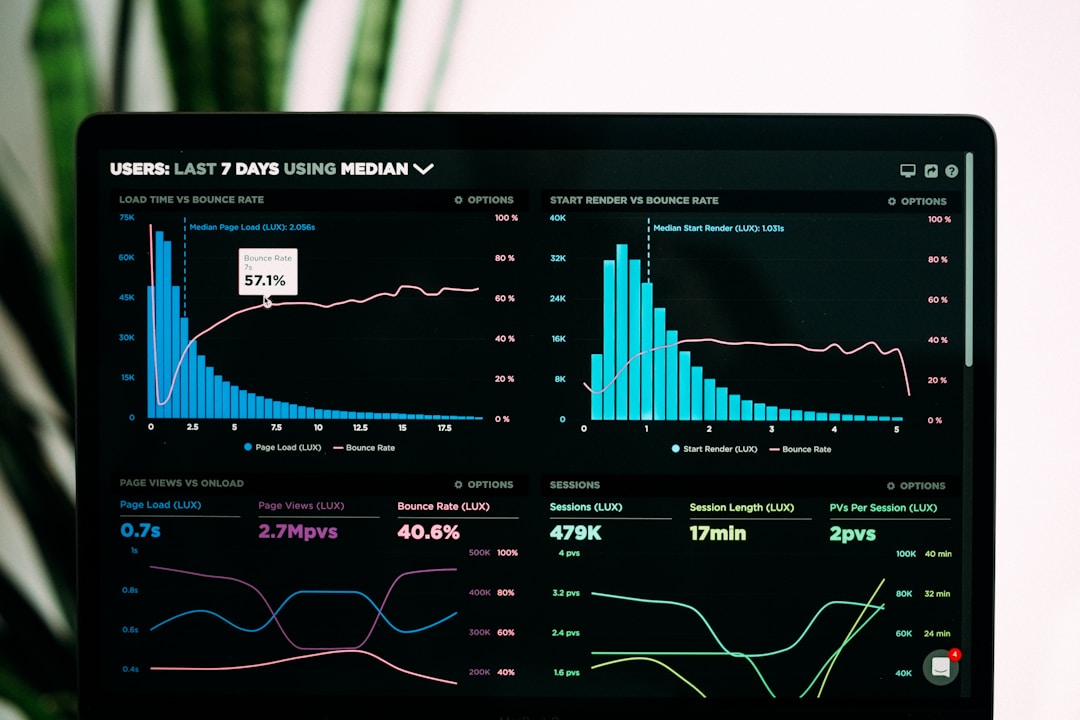
Alt Text: A screen displays two combination charts at the top.
The structure of combination charts is immensely adaptable and they can be tailored to accommodate multiple data viewpoints. There are different types of combination charts, each with a unique composition and purpose.
In a line-bar combination chart, a common axis exists on which bars and lines are plotted. Here, bars denote one measure or metric while lines denote another, thereby adequately comparing two different measurements.
On the other hand, a line-column combination chart employs both lines and columns for comparative analysis. Often, columns denote category-based data while lines show trends over a period, thus accounting for a diversified data-centric perspective.
Despite the diversity in types, the underlying goal of all combination charts remains uniform: to correlate, compare, and analyze diverse data sets to aid strategic decision-making.
Key Purposes of Combination Charts in Data Analysis
Being a remarkable blend of versatility and precision, combination charts are widely used in data analysis. They present complex data in a reader-friendly format, promoting more effortless and comprehensive data comprehension. With these charts, you’ll have a sleek and effective tool for elucidating your data story.
Accessing multiple datasets on a single axis enhances trend analysis significantly. Combination charts enable a seamless visualization of the relationship between data sets, thus providing a solid foundation for discovering patterns, movements, and correlations.
Combination charts are quite useful in unearthing and communicating insights that might remain buried in tabulated data. They make it easy for readers to grasp intricate data trends, making these charts an essential tool in data analysis and business intelligence.
Showcase of Effective Usage of Combination Charts in Business Analytics
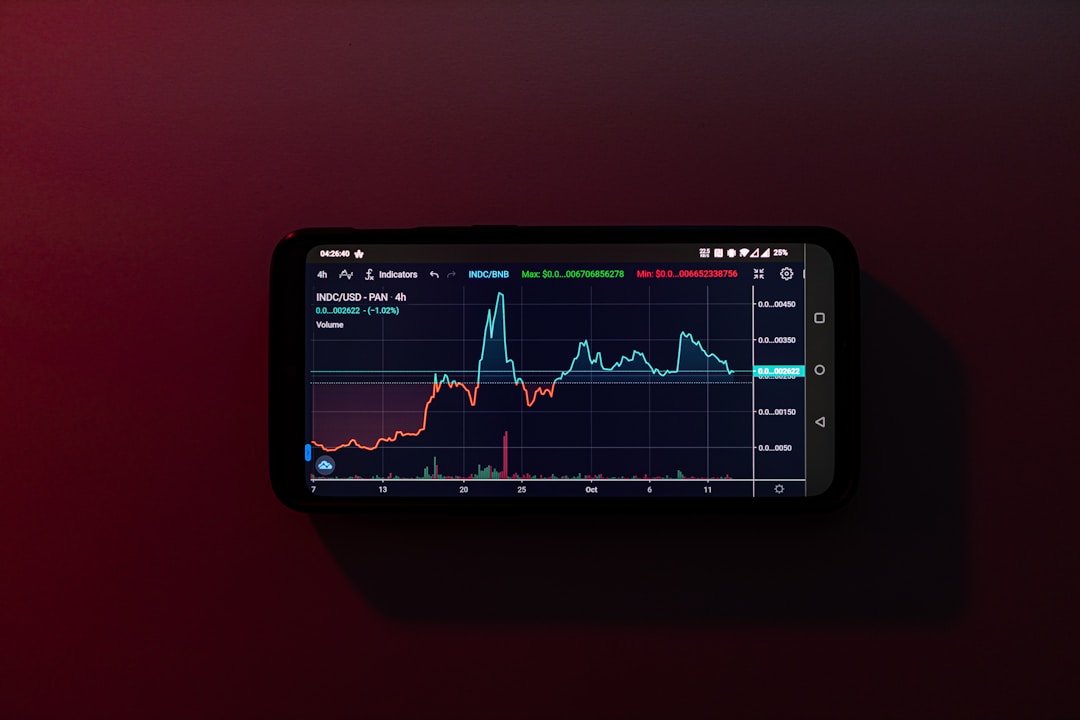
Alt Text: A combination chart on a phone.
Combination charts are instrumental in the sphere of business analytics. They offer a precise and comprehensive representation of diverse data variables, thus catalyzing the interpretation of intricate business metrics.
An excellent example is the analysis of revenue over a period, contrasted with associated expenses. A combination chart can effectively collate these two, aiding revenue optimization and cost reduction decision-making.
Moreover, in operations analysis, combination charts can showcase the production volume versus time and the corresponding defect rates. Here, the tool would help analyze performance, and in the identification and remediation of operational inefficiencies.
Thus, combination charts provide indispensable support in developing informed business strategies, enabling organizations to unlock the full potential of their data analytics process. It efficiently amalgamates complex data into visually appealing and easily comprehensible plots.

Leave a Reply