VPNs and proxy servers both safeguard user identities while providing secure access to content. Because both of these services are capable of completing tasks, they are frequently used interchangeably. One, on the other hand, preserves your privacy, while the other does not. Proxy vs VPN difference?
Proxy and VPN defined
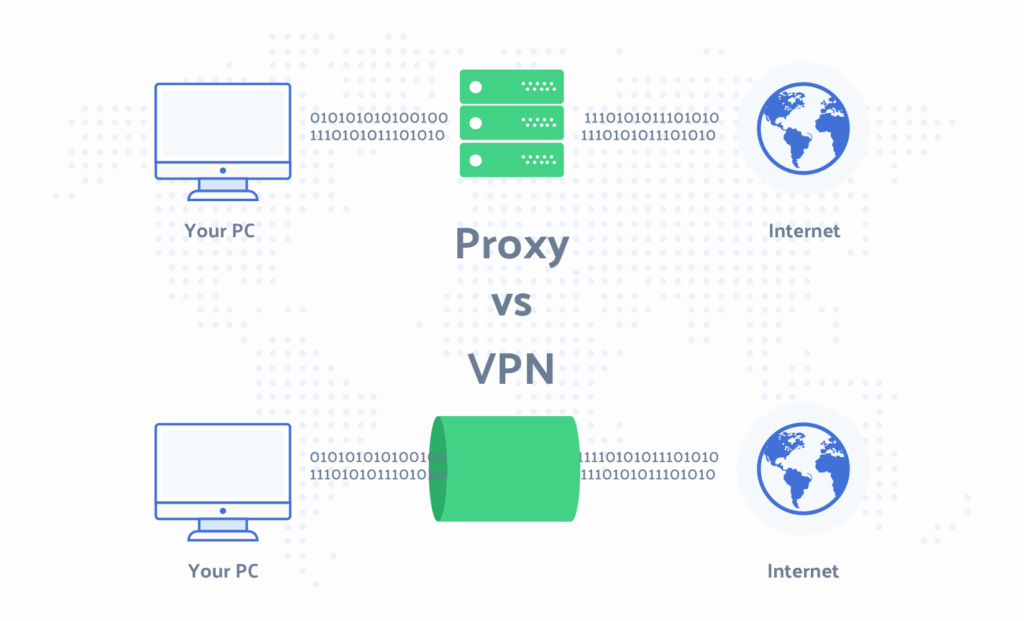
A VPN encrypts all of your network communication, whereas a proxy just encrypts application traffic. Although they both disguise your IP address, only a VPN sends your internet traffic over an encrypted tunnel. While a proxy may be used to browse the internet, it is not as safe or secure as a VPN.
A VPN will provide you with increased security as well as a variety of beneficial functions. Let’s get into the specifics of the Proxy vs VPN discussion.
What is a proxy server and how does it work?
Proxy servers work as a conduit between your device and the website you’re accessing. Your data is sent through a middleman, which is a distant computer that connects you to the host server. The web proxy server masks your real IP address so that the website only sees the proxy server’s IP address (in some cases, the computers of other proxy users are used for this). Proxy servers, on the other hand, only function at the application level, rerouting traffic from a particular app that you choose when setting up your proxy. They don’t encrypt your data either.
Proxy servers are divided into three categories:
- HTTP Proxies — These are proxies that solely provide web pages. If you configure your browser to use an HTTP proxy server, it will redirect all of your browser traffic through it.
- SOCKS Proxies — These proxies aren’t just for web traffic; they also function on the application level. Despite the fact that they can handle all types of traffic, they are frequently slower than HTTP proxies due to their popularity and heavy load.
- Transparent proxies are distinct from other types of proxies in that their consumers are generally unaware of their presence. Employers or parents that wish to monitor users’ internet activities and prevent access to specified websites might use these proxies. They are used by hotels and cafés to authenticate users on public Wi-Fi, and they may also be set up by businesses or individuals to conserve bandwidth.
What is the definition of a virtual private network (VPN)?
A VPN, like a proxy, reroutes your internet traffic through a distant server and masks your IP address so that websites are unaware of your true IP address or location (you can also check out our article on how to change your IP location for more details). It, on the other hand, acts at the operating system level, which means it redirects all traffic, whether it comes from your browser or a background programme.
Your traffic between the internet and your device is likewise encrypted using a VPN client. That means your ISP can’t see what you’re doing online – only that you’re connected to a VPN server – if they’re monitoring your internet traffic and gathering data about you. Government monitoring, website tracking, and any snoopers or hackers who might try to access your device are all protected by encryption. A virtual private network (VPN) gives you complete online privacy and security.
Because not all VPN and proxy service providers are created equal, do your homework before settling on one. Shady providers might log customers’ sensitive data, like IP addresses, DNS queries, and other details, instead of providing you with greater protection and privacy. You should avoid such providers because if their systems are hacked, they may reveal this information to law enforcement authorities, advertisers, or hackers.
Premium VPN services, such as NordVPN, work hard to secure your personal information and improve your online security. NordVPN boasts over 5,000 servers in 60 locations, allowing users to access the fastest speeds and most up-to-date features. It’s absolutely worth using the programme if you want to keep your internet traffic private and protect yourself from unscrupulous actors.
The most significant distinctions between VPN and proxy services
The following is a simple comparison of the two:
- Proxy servers do not encrypt your traffic, but VPNs do. A virtual private network (VPN) shields you from ISP monitoring, government spying, and hackers. Because proxies don’t have this capability, they should never be utilised to handle sensitive data.
- VPNs operate at the operating system level, rerouting all of your traffic through a VPN server, whereas proxies operate at the application level, rerouting only the traffic of a single programme or browser;
- Because VPNs must encrypt your sensitive data, they are slower than proxies; nevertheless, there are techniques to increase your internet connection and surfing speeds.
- Many proxy servers are free, whereas VPNs are typically expensive (you shouldn’t trust free VPN services because they have limits and tend to harvest your data).
- A VPN connection is more stable, whereas proxy server connections are more likely to go down.
Is using a VPN better than using a proxy?
Yes, a VPN is superior since it provides privacy and security by encrypting your traffic and routing it through a secure VPN server. A proxy merely routes your traffic via a mediating server, however, it does not always provide additional security. Furthermore, unlike proxies, VPNs protect all of your traffic at the operating system level. When it comes to the proxy vs VPN discussion, the latter is clearly the winner.
Is it necessary to use a proxy if you have a VPN?
No. Premium VPN services perform the same functions as proxies, as well as a lot more. For a rapid IP change, you might use a proxy extension but bear in mind that not all proxies are safe, and some of them may gather your data.
Is it possible to use a VPN and a proxy at the same time?
VPNs and proxies can be used simultaneously, although configuring them might be difficult. We also advise avoiding using it because the proxy server would merely add another middleman to your internet connection, slowing it down without providing any substantial benefits. When utilising them, it’s best to use one or the other.
Is it better to utilise a free proxy server or a free VPN?
Free Proxy vs VPN services may put your security and privacy at risk. Developers can eavesdrop on your data in the background, bombard you with advertising, or limit the amount of data you can use since they have to generate money somehow.
Premium VPNs put a lot of money into their infrastructure and offer top-notch encryption. They have a large server network, the fastest VPN protocols, and 24/7 customer service, and are constantly improving their services. We advise against using free proxies and VPNs since a few pennies saved might wind up costing you a lot more in the long run.
Conclusion
Because they both redirect your data through a distant server and disguise your IP address, a VPN and a proxy are comparable. In many ways, though, a VPN is preferable to a proxy server. Without a question, if you value your privacy and security, you should use a VPN.